Additive Manufacturing 4.0: Laser Cladding
After highlighting two of the three main technologies in additive metal manufacturing, the time has come to present the latest technique: Laser Cladding.
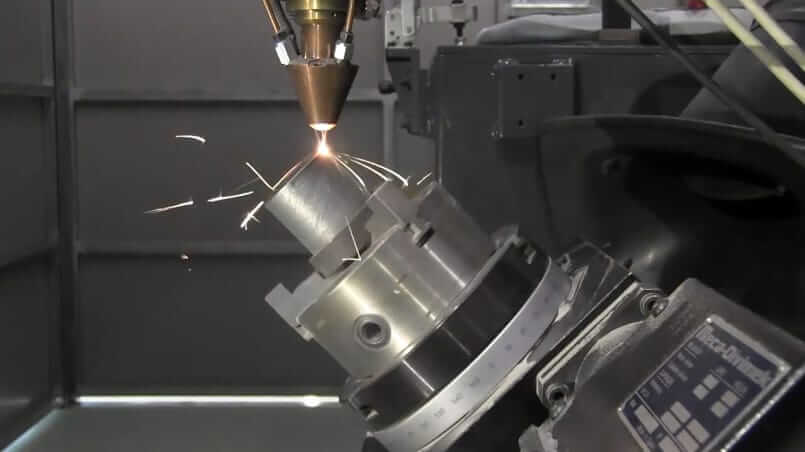
Laser Cladding consists of melting, directly, metallic powder, having previously projected it onto the surface of a base or substrate. Depending on its final use, or, saying in other words, on the characteristics of the piece on which it is to be used, the powder can be of ceramic or metallic origin.
This additive manufacturing technology, on a par with those mentioned above, uses metal as a raw material, melting only a small layer of the substrate, and obtaining deposits that conserve the properties of the metal. The dilution obtained is minimal and therefore, Laser Cladding is mainly used to improve the characteristics of a part, or even to restore it.
This technique is not used alone, but acts as a complement to other manufacturing technologies, solving problems related to porosity, thermal distortion or difficulties in processing very specific areas of a particular piece or tool.
Apart from these positive characteristics, it also allows to eliminate the mistakes of surface treatment with material contribution.
There are three main areas of industrial application of this technology:
- The reinforcement of the components, through the protection against the wear of the part.
- The repair of tools and matresses – through momentary or structural changes, in a short period of time, the drawing or mechanical adjustments of the part
- Additive manufacturing and 3D structure manufacturing
The main sectors that are incorporating this solution are Aeronautics, Automation and Renewable Energies.
Laser Cladding and the BDIH
In the Basque Country, there is a great deal of knowledge and experience in the application of this technology in manufacturing processes.
At the University of the Basque Country, there is a LMD System for Additive Manufacturing by the AKTINOS 500 Laser Cladding, a 5-axis system with a working volume of 600x400x400mm and a capacity of A± 110°/C360° rotary axes. The services offered by the asset include the design of filler nozzles, advice on the fine-tuning of material filler systems, design and sizing of equipment; comparative analysis of the LMD process against other additive manufacturing processes; characterisation of mechanical and metallurgical properties, process capabilities and requirements; additive manufacturing of structures by means of LMD in different alloys and geometries; customised training in LMD technology, applications, equipment, programming, strategies, handling and management of dust; and the improvement of tribological properties of complex components by means of laser contribution for the improvement of tribological properties (friction, thermal,…) by means of the contribution of ceramic materials.
Tekniker, on the other hand, has a Robotic Cell for the construction of large components by concentric wire deposition, which allows a 3D metallic impression of large parts by Laser Cladding on wire – the robotic cell works with 6 degrees of freedom, has an additional tilt and turning table for the construction of large components (up to 1m3 in volume approximately) at high deposition rates of up to 6kg/h. The services offered by the asset include the construction of large 3D geometries; the demonstration of large component construction by concentric wire deposition; the development, testing and validation of equipment and special technology (heads, optics) for deposition in special environments or geometries; the adaptation of machinery for the inclusion of wire deposition heads by LMD; the development of deposition parameters and strategies for LMD in wire of new metal alloys; the subsequent testing (metallography, fatigue, mechanical characterization, etc.); the development of closed-loop control systems for geometric and thermal control of the deposited material and practical training in the whole process (design, calculation, material analysis, process, coatings, NDT) of construction of large components by concentric wire deposition.
Here is just a sample of how the BDIH¨s Additive Manufacturing node allows Basque companies to incorporate new models, concepts and techniques in the way they produce their parts and products.
If you are interested in exploring what the node offers, follow this series of articles on Additive Manufacturing 4.0 where we tell you in detail what its capabilities, assets and services are in a practical and personally tailored way.
Contact the BDIH to find out how we can bring your company closer to the solutions that interest you most.
Related news
SMARTPM and SubAero Precision Machining announce strategic partnership in India
The collaboration between SMARTPM and SubAero Precision Machining (Group Designcell) is a big step in our global growth, helping us establish a strong foundation in one of the world's fastest-growing industrial markets

Companies with greater gender equality perform better in terms of innovation and are more competitive
The study of the SPRI initiative "Women in Industry" shows that gender equality has an impact on the improvement of company results.

SPRI presents the results of the study on the impact of women on industrial competitiveness at the World Manufacturing Forum
The reports is the continuation of the work carried out by the SPRI Group and the Foreign Network office in Milan since 2020 as leader of the Women in Manufacturing expert group.

Europako fabrikazio-ikerketaren etorkizuna
Donostian, egunotan, MANUFUTURE Conference 2023 egiten ari da, hau da, fabrikazio-industriaren etorkizunari buruzko Europako konferentzia.

Basque Open Industry will show Europe its industrial and technological ecosystem at the European SME Week (SME Week) from 13 to 17 November.
Talent, internationalisation, energy-environmental and technology-digital transitions. SME Week 2023. Exhibition and stands at the BEC: “Rebuild Ukraine”.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: 5-axis multi-process milling cell, capable of very high speed operations
The University of the Basque Country offers Basque companies, via the BDIH, the possibility to have at their disposal a 5-axis multi-process milling cell, capable of very high-speed operations.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Inspection/measurement robotic cell using non-destructive techniques
Tekniker gives the opportunity to Basque companies, by means of the BDIH, of having at their disposal a cell which permits to carry out analysis for the quality control and the non-destructive inspection of pieces.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Equipment/Techniques/Methodologies for the study and evaluation of corrosion
Cidetec offers Basque companies, through the BDIH, the possibility of testing their materials with in the order to know their corrosive capacity. For this purpose, the asset uses accelerated and cupro-acetic corrosión climatic chambers, as well as electrochemical and localized techniques for the corrosion studies.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Systems for mechanical properties and microstructure determination by magnetic non-destructive measurements
CEIT offers companies, through the BDIH, the possibility of access to quality control systems to detect failures or inspect subsurface processes in a non-destructive manner, allowing costs to be reduced and avoiding wasting parts that could be sold

The Enterprise Europe Network offers Basque companies advice on technological development and the international commercialization of innovative products and services
The Enterprise Europe Network (EEN) has established itself as the perfect public sector tool to complement the efforts of Basque companies in internationalizing their R&D&i and their business in general. Through its advisory and assistance service in the transfer of knowledge, technology and innovation, more and more SMEs are seeing...