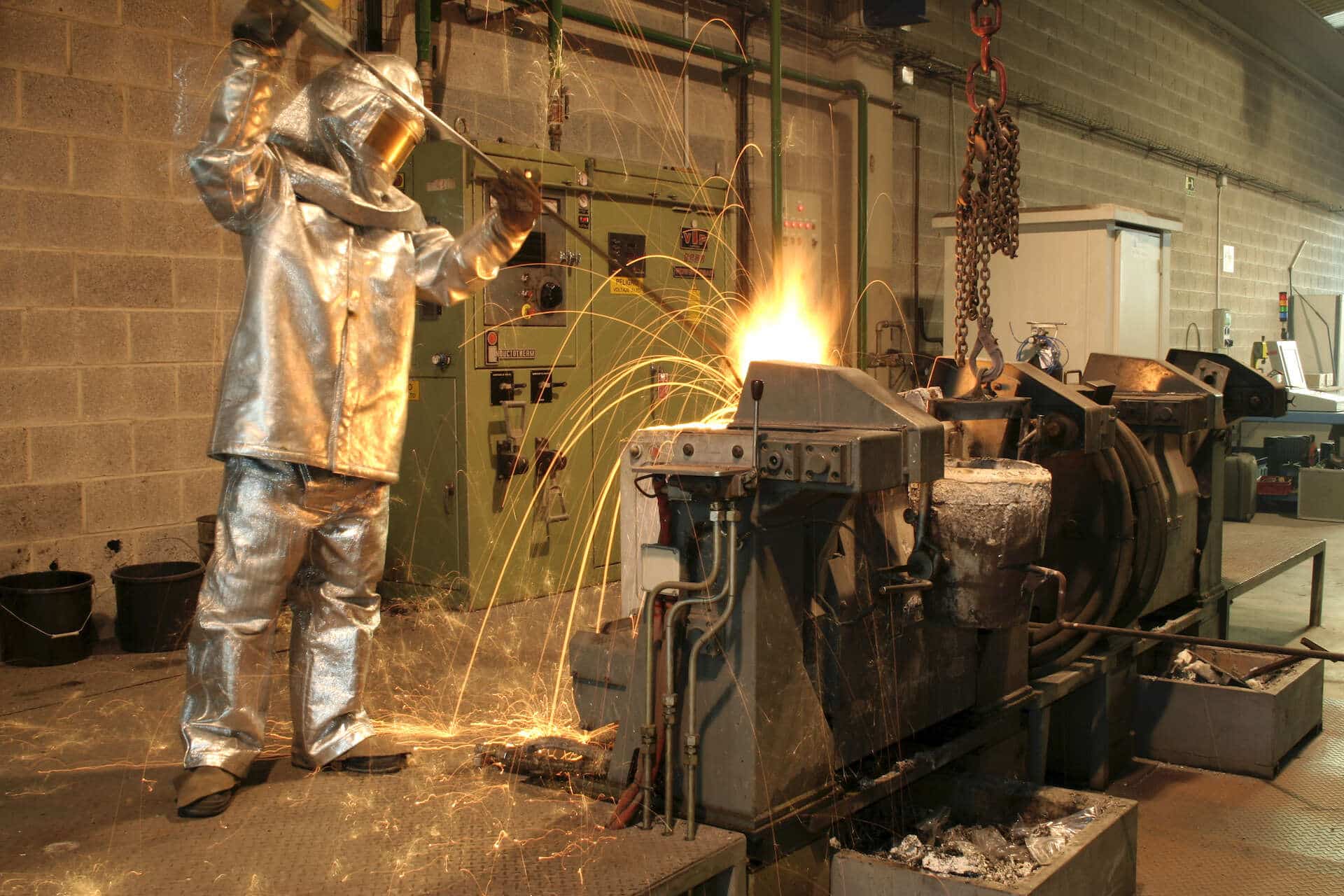
Materials 4.0: Combine new and different materials to meet the challenge of manufacturing parts
 In this article, SPRI Group, together with the BDIH and its Advanced Materials Node, shows manufacturing companies how to address the challenges of using different materials in the same part or structure and increase their product value, adapting both the processes of joining materials and the company’s own manufacturing processes to new design and manufacturing strategies.
In this article, SPRI Group, together with the BDIH and its Advanced Materials Node, shows manufacturing companies how to address the challenges of using different materials in the same part or structure and increase their product value, adapting both the processes of joining materials and the company’s own manufacturing processes to new design and manufacturing strategies.
The search for product improvement is an essential activity for a company to remain relevant. According to the Spanish Technological Strategy for Advanced Materials and Nanomaterials – MATERPLAT; “…the competitiveness of many of the large industrial sectors […] depends to a great extent on their capacity to generate innovations in materials, including all their associated processes, which becomes even more pressing if we take into account that the business sector finds it increasingly difficult to compete in costs in a global economy such as the present one”.
To achieve improvements in product performance or migrate to new materials, it is essential to embark on a process of discovery and experimentation with new design and manufacturing strategies. These, in turn, demand more reliable and versatile methods of joining materials, which allow different materials to be used in combination in parts.
On the other hand, the demand for hybrid joints is continuously growing because, for many sectors, the applications and performance of existing materials separately do not allow the necessary requirements to be met, the ideal being the fusion of different materials. Therefore, the combination of dissimilar materials can in many cases open up a new field of possibilities in which to develop tailor-made materials for a specific application or component. The value sought is to develop products with better performance, more durable and sustainable to help them compete in a global market.
When joining different materials, we must combine: resistance and durability; design and aesthetics; low weight and efficiency; assembly and manufacture; cost-efficiency. The members of the BDIH’s advanced materials node have a series of assets and teams of experts specialised in different joining techniques that are available to Basque industry. The techniques and associated services presented in this article cover fusing by co-moulding, fusion by diffusion, structural joins based on adhesives and inspection techniques by means of acoustic emissions, and dissimilar joins by FSW (Friction Stir Welding).
AZTERLAN has assets that allow the joiningw of dissimilar metallic materials by co-moulding, a technique that consists of introducing a metal part in a solid state into a casting mould into which the metal is poured in a liquid state, giving rise to a bimetallic part.
This type of work can be carried out in your Pilot Casting Plant for the development of new materials and casting technologies on an industrial level. The infrastructure has all the necessary means for the melting, casting and solidification of new alloys into test pieces, demonstrators and prototypes of any alloy based on Fe (iron), Al (aluminium), Cu (copper) and/or Ni (nickel). The infrastructure provides three main types of service: the development and validation of new Fe/Al/Cu/Ni alloys including other metals, the development of new casting technologies and the rapid prototyping of new components according to the customer’s requirements.
CEIT has a Mechanical Reliability and Structural Integrity Unit, an asset that has the equipment which allows working around diffusion bonding, a technique that involves the application of high temperatures and pressures to similar or different metals that are coupled in a hot press, and that makes the atoms of the solid metal surfaces interleave and join. This asset allows the mechanical characterization of materials and components, and has several fatigue machines, an Ion Focused Beam Micromachining (FIB) machine, and a Nano-Indenter and Tribo-Indenter, Hysitron. The services offered by this asset to the Basque industry are the analysis of in-service components and forensic failure analysis, mechanical and structural characterisation of surfaces and coatings, and the measurement of mechanical properties and their dispersion in operating conditions, minimising the safety coefficients and costs of production, maintenance and life prediction of components using this and other joining techniques.
IKERLAN, on the other hand, offers a Laboratory for the characterisation of mechanical and acoustic properties of materials, where structural joins based on adhesives and inspection techniques by means of acoustic emissions can be studied. This laboratory offers services of acoustic tests, evaluation of structural integrity (acoustic emissions), measurement of deformations on 2D and 3D surfaces of all types of materials, as well as the measurement of residual surface tension (up to 2 mm deep) in diverse materials and composites.
LORTEK has a pilot plant for the study of advanced joints using techniques such as arc, laser and friction welding (FSW), resistance joins and solid state joins, among others. This asset provides the Basque industry with the capacity to develop feasibility studies of advanced joints with dissimilar materials and with new materials. The services offered range from the study of the possibility of making a combination that meets the required functionalities, with different technologies and processes, to a proof of concept, to the analysis of its industrialisation.
Finally, TECNALIA has a Multimaterial Joining Centre that offers feasibility analysis services for multimaterial joins, that is, the study and development of advanced solutions for multimaterial joins (metal-metal, metal-composite) based on the different technologies available (adhesive joint, laser joint, VCSE (Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting laser) join, mechanical join, forming join, etc.) and their combination. This asset includes all the process stages: material compatibility, characterization of joins and materials, process simulation, functionalisation of surfaces for resistance improvement, implementation of the appropriate bonding method, supervision and control of the main relevant parameters, etc.
If you are interested in deepening your knowledge of what the Advanced Materials Node of the BDIH offers, follow this series of articles on Materials 4.0 where we tell you in detail which are the capacities, assets and services of the node in a practical, applied way.
Contact the BDIH to find out how we can bring your company closer to the solutions that interest you most.
Related news
SMARTPM and SubAero Precision Machining announce strategic partnership in India
The collaboration between SMARTPM and SubAero Precision Machining (Group Designcell) is a big step in our global growth, helping us establish a strong foundation in one of the world's fastest-growing industrial markets

Companies with greater gender equality perform better in terms of innovation and are more competitive
The study of the SPRI initiative "Women in Industry" shows that gender equality has an impact on the improvement of company results.

SPRI presents the results of the study on the impact of women on industrial competitiveness at the World Manufacturing Forum
The reports is the continuation of the work carried out by the SPRI Group and the Foreign Network office in Milan since 2020 as leader of the Women in Manufacturing expert group.

Europako fabrikazio-ikerketaren etorkizuna
Donostian, egunotan, MANUFUTURE Conference 2023 egiten ari da, hau da, fabrikazio-industriaren etorkizunari buruzko Europako konferentzia.

Basque Open Industry will show Europe its industrial and technological ecosystem at the European SME Week (SME Week) from 13 to 17 November.
Talent, internationalisation, energy-environmental and technology-digital transitions. SME Week 2023. Exhibition and stands at the BEC: “Rebuild Ukraine”.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: 5-axis multi-process milling cell, capable of very high speed operations
The University of the Basque Country offers Basque companies, via the BDIH, the possibility to have at their disposal a 5-axis multi-process milling cell, capable of very high-speed operations.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Inspection/measurement robotic cell using non-destructive techniques
Tekniker gives the opportunity to Basque companies, by means of the BDIH, of having at their disposal a cell which permits to carry out analysis for the quality control and the non-destructive inspection of pieces.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Equipment/Techniques/Methodologies for the study and evaluation of corrosion
Cidetec offers Basque companies, through the BDIH, the possibility of testing their materials with in the order to know their corrosive capacity. For this purpose, the asset uses accelerated and cupro-acetic corrosión climatic chambers, as well as electrochemical and localized techniques for the corrosion studies.

Get to know the assets of the BDIH: Systems for mechanical properties and microstructure determination by magnetic non-destructive measurements
CEIT offers companies, through the BDIH, the possibility of access to quality control systems to detect failures or inspect subsurface processes in a non-destructive manner, allowing costs to be reduced and avoiding wasting parts that could be sold

The Enterprise Europe Network offers Basque companies advice on technological development and the international commercialization of innovative products and services
The Enterprise Europe Network (EEN) has established itself as the perfect public sector tool to complement the efforts of Basque companies in internationalizing their R&D&i and their business in general. Through its advisory and assistance service in the transfer of knowledge, technology and innovation, more and more SMEs are seeing...